How Do VelocityShares’ EVIX And EXIV Work?
Vance Harwood | Aug 20, 2017 05:25AM ET
In May 2017 VelocityShares introduced two new volatility funds, EXIV (NYSE:EXIV) and EVIX (NYSE:EVIX), which track European volatility futures. In digging into these funds I’ve encountered a dense mashup of the familiar and the foreign.
The differences between European Volatility futures and VIX futures are relatively small so it’s reasonable to view EXIV and EVIX as close cousins of VelocityShares’ XIV and Barclays’ VXX, however, these funds depend on a set of securities and processes with subtle and not so subtle differences with the mainstay USA volatility funds.
If you are not familiar with VIX futures based volatility Exchange Traded Products (ETPs) then I recommend you first take the time to read these posts on VelocityShares’ XIV and Barclays’ VXX before you tackle these new arrivals.
- How does XIV work?
- How does VXX work?
Some Basics
- EVIX is a short-term long volatility fund that will tend to go up if European stocks go down significantly.
- EXIV is a short-term inverse volatility fund that tracks the opposite of EVIX’s percentage moves on a day only basis. Because EVIX adjusts its assets at market close to achieve its daily tracking goal it does not behave like a true short of VIX, which can be a good thing or a bad thing depending on the market moves.
- The Swiss bank, UBS AG, is the issuer of both of these Exchange Traded Notes (ETNs). They are structured as unsecured long term debt securities. As of August 2017, Moody’s rating of UBS’ long term debt was: “A1 Not on Watch.” The investor fee charged by UBS AG is 1.35% annualized for EVIX and EXIV, this compares to 1.35% for XIV and 0.89% for VXX.
- The European Volatility futures that these funds track settle at expiration to the European volatility index VSTOXX. VSTOXX uses a methodology very similar to the CBOE’s VIX but instead of being based on the prices of S&P 500 (SPX) options the VSTOXX is based on STOXX option prices.
- The STOXX index is comprised of 50 of the largest companies in the Eurozone and is capitalization weighed like the S&P 500. It does not include companies from the UK. These 50 stocks represent around 60% of the Eurozone stock market value. In comparison, S&P 500 represents around 80% of the total USA stock market capitalization. Similar to the S&P 500 index, the STOXX index does not include dividends, so the returns of actually holding the constituent stocks would be higher than the index indicates. For the last 5 years, the STOXX dividends have averaged 2.5% vs 1.9% for the S&P 500.
- EVIX and EXIV track indexes (VST1MSL & VST1MISL respectively) that theoretically hold a mixture of the two VSTOXX futures nearest to expiration. The mixture gives an expiration horizon of 30 days, similar to the VIX future based short term volatility funds like VXX and XIV. These funds are fully divested out of expiring futures the day before their expiration/final settlement.
- Both funds effectively do a daily end-of-day rebalance that adjusts the number of volatility contracts that they hold in order to maintain a 30-day average horizon. At the same time EXIV also does an asset rebalance such that its daily percentage move will closely match the opposite of EVIX’s next day daily percentage move (see How Does XIV Work? for more on this).
- Standard processes and rough equivalences in key securities
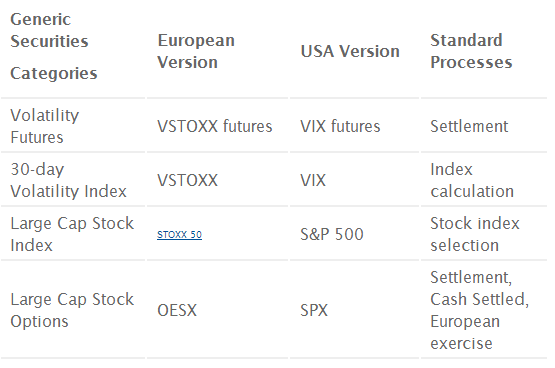
-
- The key securities and processes are similar between the European and USA markets but in no case have I found a pair of processes that are identical. For example, VIX futures settle to a special opening quotation of the CBOE’s VIX® soon after market open on expiration days whereas VSTOXX futures final settlement price is determined by the average VSTOXX index level between 11:30 and 12:00 CET on the day of expiration.
-
- A significant difference between the VIX and the VSTOXX index is that the VSTOXX calculation does not incorporate options with bid prices below 50 Euro. This contrasts with the VIX’s calculation which uses options with bids as low as $5, which increases the chances that an institutional player might attempt to influence the VIX’s settlement value in their favor by buying or selling cheap out-of-the-money puts.
- Quotes / Historical Data
- While free quotes for EXIV and EVIX are easy to get with the usual sources (Online brokers, Yahoo (NASDAQ:AABA), Google (NASDAQ:GOOGL)), obtaining quotes for the underlying securities/indexes is tougher. The ones I’ve found so far are:
- STOXX
- Quotes Yahoo Finance (ticker ^STOXX50E)
- Historical Data: Investing.com
- VSTOXX (ticker V2TX or DVY00)
- Quotes and one year of historical data FT.com
- Quotes of spot and futures Barcharts.com
- Historical data (back to 2009) STOXX.com
- VSTOXX Futures
- Quotes of spot price and futures Barcharts.com
- Euroexchange.com
- VST1MSL (EVIX’s dollar denominated index)
- Quotes STOXX.com
- Historical data STOXX.com
- VST1MISL (EXIV’s dollar denominated index)
- Quotes STOXX.com
- Historical data STOXX.com
- Intraday Indicative value (IV) quotes for EXIV and EVIX are available from some brokers and Yahoo Finance. The symbols within Yahoo are ^EXIV-IV and ^EVIX-IV
Hours Typically the European continent is 6 hours ahead of USA Eastern time. Standard closing time on the European continent exchanges is 5:30 PM, so they are closing at 11:30 Eastern time. The IV values for EXIV and EVIX don’t update after 11:30 ET because the OESX options used to compute VSTOXX are not trading past then. The Yahoo finance chart below illustrates EXIV’s IV value flat-lining during the afternoon.
- The VSTOXX futures referenced by these funds trade from 7:30 to 22:30 CET.
- Termination risk
- Along with XIV and ProShares’ SVXY, EXIV will terminate if there is a large enough volatility spike. The funds are guaranteed to not go below zero and the issuers will not commit extra capital to meet margin calls in that sort of extreme situation. In EXIV’s case, the fund will be automatically terminated if the drop in the intraday IV value is 75% or more from the previous day’s close. For the USA markets, historical data suggests it would take a VIX intraday spike of at least 166% to result in a 75% drawdown in the inverse volatility funds and I suspect that the VSTOXX/ VSTOXX futures sensitivities are similar. In the case of termination shareholders would receive the net value of the fund after the transactions settle from that event. The value is not guaranteed to be 25% of the previous day’s value, it is only guaranteed to be zero or higher.
Comparing Markets—and Indexes
The chart below compares the historical values of the S&P 500 and the STOXX as well as the VIX and VSTOXX since January 1998.
- A few things stand out when looking at the STOXX (red line)
- The STOXX fully participated in the 2000 dot com crash and the 2008/2009 bear markets
- The STOXX is still well below its 2000 highs—the lack of recovery in the STOXX after the 2008/2009 financial crash is striking
- Looking at VSTOXX (purple) vs the VIX (black) above:
- The VSTOXX shows mean reverting behavior similar to the VIX. Sharp spikes up are followed by fairly rapid decays towards the mean values.
- Periods of low volatility can persist for a long time but eventually, the VSTOXX reverts back to values closer to the mean
- Generally, the VIX and the VSTOXX are closely correlated
- The VSTOXX value is almost always higher than the VIX’s value
- Some statistics for the S&P 500 and the STOXX, January 1999 through July 2017:
Statistics for the VIX and the VSTOXX, January 1999 through July 2017:
- A few observations:
- The VSTOX distribution is shifted notably higher in value than the VIX
- While the two index distributions have truncated left “shoulders” and big fat tails on the right the VSTOXX has a significantly more balanced distribution around its mean compared to the bottom heavy VIX.
- The difference between the mode (the most common value rounded to 0.1 pts) and the record low is only 36% with the VIX compared to 107% for the VSTOXX
Historic Performance
- By using a simulation starting in June 2009 of the indexes that EXIV and EVIX are based on we can get a feel for their performance relative to XIV and VXX. The only difference between the indexes and the EVIX/EXIV ETNs is that the investor fees and treasury bill interest are not included in the index values. The chart below shows relative performance when starting with portfolios of $10K fully invested in each of the funds.
- The two lines starting high on the left (green and purple lines) are long volatility funds that reference the left axis scale. The long volatility funds exhibit the typical long volatility fund race to zero, with VXX slightly better at losing value.
- The two inverse volatility funds (red and blue lines) referencing the right scale perform much better than the long funds. Overall XIV’s performance dominates with an approximate 40X growth since 2009.
Using a log scale on the vertical axis provides a much more accurate visual way to judge relative performance. The first chart shows VXX index vs the EVIX index
- The two portfolios begin diverging in early 2010 and don’t return to a similar loss rate until 2016.
- Over the 2010 to 2015 period EVIX’s decay rate was significantly lower than VXX’s. It’s likely that the VSTOXX futures had considerably lower contango levels during that period compared to the VIX’s futures
- Looking at the inverse volatility story with a log scale tells a similar tale except that the portfolios diverge almost immediately after the simulation is started.
Similar to the long side of the things, since around January 2016, the performance of the two inverse funds has been pretty close. Starting the portfolio simulation for both the long and inverse funds in January 2016 suggests that the USA and European based funds would have tracked relatively closely since then. The chart below shows the result of the simulation.
When to Use These New Funds
- An obvious application for these new funds is placing a bet on an upcoming European event with potentially major impact (e.g., a Brexit vote, or the Le Pen / Macron election). In “known/unknown” cases like this the date of the event is well known, but the result is uncertain and potentially economically impactful. It’s certain that the VSTOXX will go up before an event like this, the interesting, and potentially lucrative question is what will happen to volatility after the event—panic/distress or a collapse back to the status quo.
- Diversification is another application. Obviously, the European markets are not in lockstep with the USA markets and this distance will tend to smooth out some of the volatility shocks. For example, XIV dropped 17.8% on May 17th, 2017 from its previous close, but EXIV only dropped 9.2%. A portfolio holding both XIV and EXIV would have some cushioning against these sorts of glitches.
- Having EVIX and EXIV gives traders a way to profit if they see an upcoming convergence or divergence between the volatility indexes in the two markets. For example, if you believe a recent volatility jump in USA markets will propagate to the Europe you could do a straight EVIX purchase or a pairs trade between EVIX and a long volatility fund like VXX.
- It might be possible to do some form of contango arbitrage with these funds. It’s certain that the contango losses/gain won’t be identical between the two sets of futures markets, a pairs trade might allow a trader to profit from the difference in contango rates with an overall reduced risk exposure.
Oddities
- There are differences in the trading hours of these two markets. On the USA side of things, the Intraday Indicative (IV) quotes will be frozen on EVIX and EXIV past the normal close of the European markets, depriving us of an important piece of trading information that’s useful for trading low volume ETPs like these. On the European side, we have times when the volatility securities are trading while the USA markets are closed. For example, you might want to close out EXIV positions if the STOXX was crashing, but if the USA markets are closed there would be no direct way to do that.
- Since VSTOXX futures are denominated in Euros and EVIX/EXIV are dollar-denominated, exchange rate changes will have effects, although compared to the normal hysteria of volatility markets I doubt it will be significant. Since EXIV is effectively short VSTOXX futures the impact of currency rate changes will be in the opposite direction of EVIX which holds long positions.
- The EVIX/EXIV calculations assume that cash not needed for margin on the futures will be “invested” in short term German treasury bills, which have been running at negative interest rates (currently -0.734%). Negative rates will result in a minor drag on these fund’s values.
- Options are available on EVIX, but not on EXIV. You might guess that the CBOE shies away from options on inverse volatility funds because of their termination risk, but options are offered on ProShares’ SVXY so this argument doesn’t hold up. On the same subject, it’s ridiculous that the CBOE does not offer options on XIV, a well-established fund with hundreds of millions in assets.
Conclusion
It’s head spinning to introduce a whole new set of securities and indexes into the already confusing area of volatility investing but as I reviewed the different ways to use EVIX and EXIV it appears well worth the trouble to learn a few new things. These funds open up new volatility based opportunities in geographic based investing, diversification, and arbitrage style trades.
Trading in financial instruments and/or cryptocurrencies involves high risks including the risk of losing some, or all, of your investment amount, and may not be suitable for all investors. Prices of cryptocurrencies are extremely volatile and may be affected by external factors such as financial, regulatory or political events. Trading on margin increases the financial risks.
Before deciding to trade in financial instrument or cryptocurrencies you should be fully informed of the risks and costs associated with trading the financial markets, carefully consider your investment objectives, level of experience, and risk appetite, and seek professional advice where needed.
Fusion Media would like to remind you that the data contained in this website is not necessarily real-time nor accurate. The data and prices on the website are not necessarily provided by any market or exchange, but may be provided by market makers, and so prices may not be accurate and may differ from the actual price at any given market, meaning prices are indicative and not appropriate for trading purposes. Fusion Media and any provider of the data contained in this website will not accept liability for any loss or damage as a result of your trading, or your reliance on the information contained within this website.
It is prohibited to use, store, reproduce, display, modify, transmit or distribute the data contained in this website without the explicit prior written permission of Fusion Media and/or the data provider. All intellectual property rights are reserved by the providers and/or the exchange providing the data contained in this website.
Fusion Media may be compensated by the advertisers that appear on the website, based on your interaction with the advertisements or advertisers.